EIRA Quick Guide: Enabling Tools and Resources
Introduction
In this section, we’ll share some of the tools and resources we think can be useful for academics, knowledge exchange professionals and enterprise staff to use when working with external businesses.
If you’ve read our other guides, some of these will feel familiar, but this guide provides a central space for them to be found quickly and easily.
Enterprise
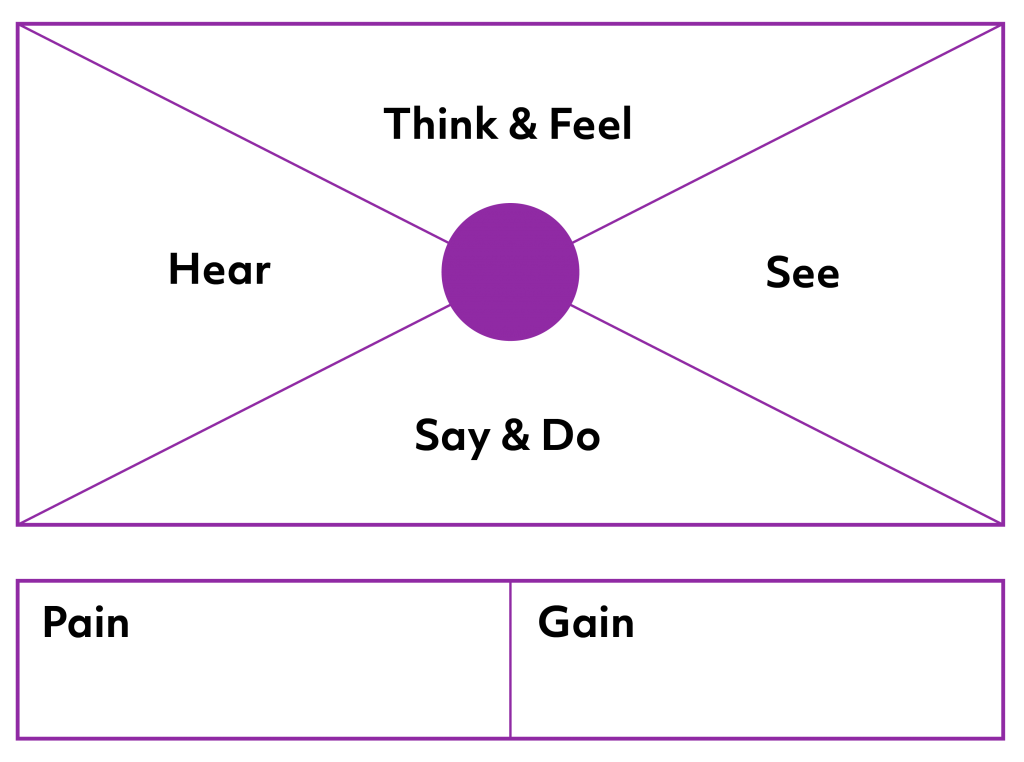
Customer Empathy Map
Consultancy and Knowledge Exchange
Creative Problem Solving (CPS)
Creative Problem Solving (CPS) is a way of using your creativity to develop new ideas and solutions to problems. The process is based on separating divergent and convergent thinking styles, so that you can focus your mind on creating at the first stage, and then evaluating at the second stage.
Divergent thinking is the process of generating lots of potential solutions and possibilities. Convergent thinking involves evaluating those options and choosing the most promising one.
Innovate UK: Innovation Canvas
Innovate UK have developed an “Innovation Canvas” which helps businesses focus on the factors that can affect new business opportunities, ideas or concepts, by examining what the opportunities within the market are, what the business has to offer and what the business’ capabilities are. These can be narrowed down to Top Challenges and Action Points, as shown in the table. The Canvas can help to:
- Act as a stimulus for discussion,
- Examine the strengths and weaknesses of the proposal
- Explore the potential benefits and challenges that might face the project
- Assess the resources available
- Help the business prioritise issues that are most likely to impede progress
- Focus on the “Top Challenges” to identify “Action Points”. This involves asking the question‘ what can be done to overcome the challenges?’. Alternatively, any gaps identified can be listed in Top Challenges.
Key Areas of Focus
When using the Innovation Canvas toolkit, there are several discussion points you could use to focus on:
Innovation Design
- Search for unmet needs and new opportunities
- Generate ideas for new products and services
- Suggest new uses for existing business capabilities
- Design innovations for commercial success
Innovation Diagnosis
- Identify and overcome important challenges
- Spot gaps in your capacity to innovate
- Test assumptions that may be hindering progress
- Clarify areas of risk and uncertainty
- Invite and secure team buy-in
MoSCoW
The MoSCoW method is a prioritization technique used to focus discussions and reach a common understanding with clients on the importance they place on the delivery of each element of the requirement. It is also known as MoSCoW prioritization or MoSCoW analysis.
The term MoSCoW itself is an acronym derived from the first letter of each of four prioritization categories (Must have, Should have, Could have, and Won’t have). This technique lists all the requirements, features or aims of the project, then works out a priority list of what must be included, what should be included, what could be included and won’t be included- but may still be relevant.
Managing Expectations
Managing expectations is a key part of any project, particularly when gathering requirements or setting the scope of the project. It is easy to be carried along with someone else’s enthusiasm and passion for an idea or for you to be carried along with you own ideas, which can develop and expand to well beyond what can be achieved within the time and available resources. Ensuring everyone is clear from the start as to what is to be achieved, can in the long run, avoid disagreements and acrimony, which can damage or even destroy confidence and trust between yourself and the client. A good technique to help with this is to be “S.M.A.R.T.” a mnemonic which can help provide a framework for setting of objectives.
S.M.A.R.T

GANNT Charts
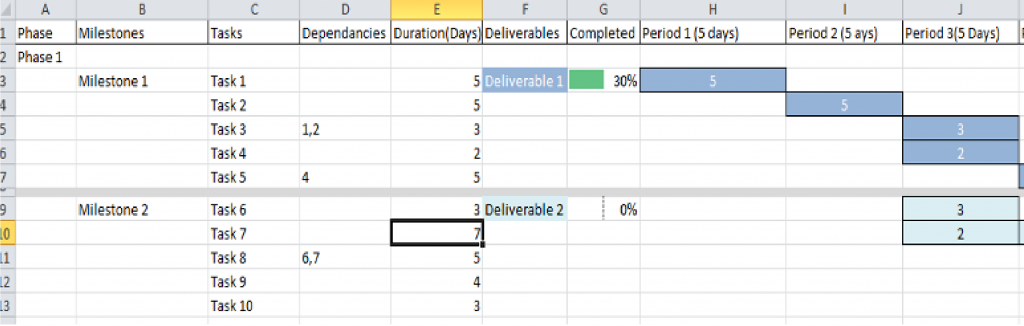
GANNT Charts can be used to show project Phases, Milestones and Tasks, in a visual format displaying resources, dependency and duration as a bar chart. They are an excellent means of representing, in an easily digestible way, the tasks, dependencies and time for each milestone (deliverable).
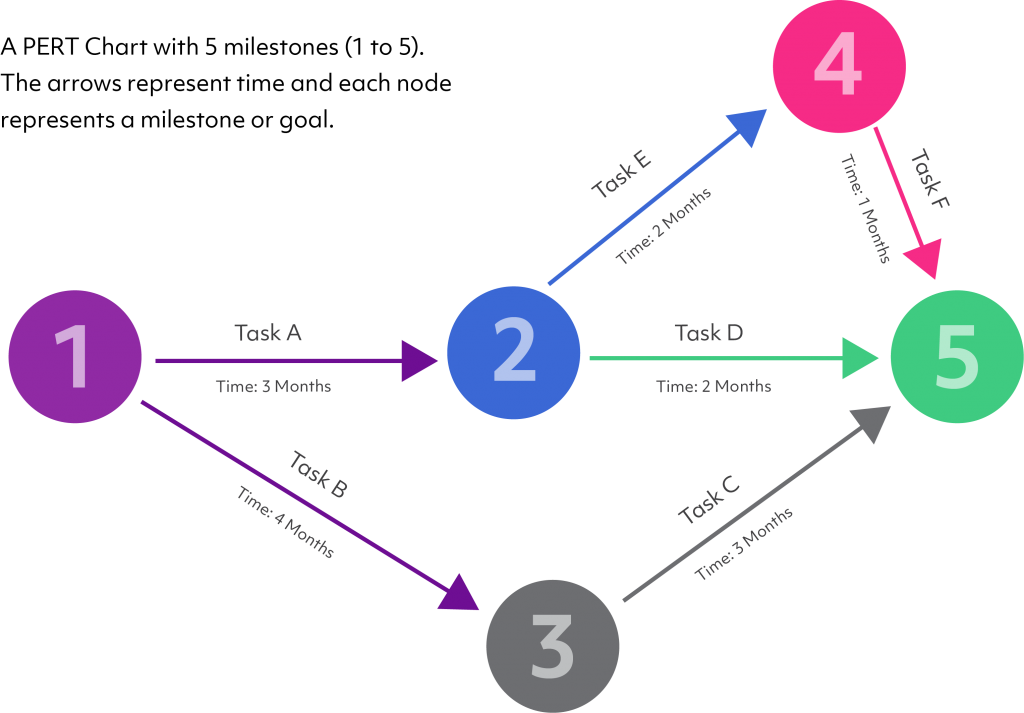
PERT Chart
PERT stands for Project Evaluation and Review Technique and is a method of analysing the tasks involved in completing a given project, based on the time needed to complete each task, and to identify the minimum time needed to complete the total project. It is an event-oriented technique rather than start- and completion-oriented, and is used more in those projects where time is the major factor rather than cost. It is most commonly applied to very large-scale, complex projects or Research and Development projects. PERT is a management tool, which uses an arrow and node diagram of activities and events: arrows represent the activities or work necessary to reach the events or nodes that indicate each completed phase of the total project.
Business Engagement

Summary
In this guide we’ve covered some of the helpful tools and resources our research, enterprise and knowledge exchange staff often use to plan projects.
Check with your institution to find out more about the tools, resources and project management systems that are used by your teams to set clear boundaries and timelines.
